![[Return to top]](../../epc.png) 68008 Dartboard control pcb. By Lee Davison.
68008 Dartboard control pcb. By Lee Davison.
Back
![[Return to top]](../../epc.png) 68008 Dartboard control pcb. By Lee Davison.
68008 Dartboard control pcb. By Lee Davison.
Back
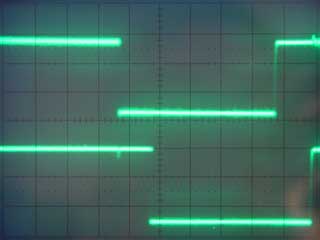
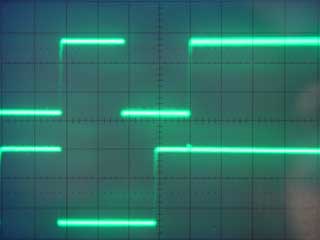
This is the code that drives the I2C bus on th edart control board. The routine Getadrak is to allow access to the bus via the USR() function in EhBASIC.An example of it's use can be found here.
I2C Waveforms.
![[e-mail]](../../eml_sm.png)